In the dynamic realm of geography and spatial analysis, Geographic Information Systems (GIS) stand as an indispensable tool, transforming the way we perceive and interact with our surroundings. In this exploration, we delve into the world of harnessing GIS technology for effective topographic map creation, unlocking its potential to revolutionize mapping processes. From visualizing landscapes to making informed decisions, GIS emerges as a powerful ally in the cartographer’s toolkit. Let’s navigate through the intricate layers of GIS mapping and understand how it shapes the future of topographic representation.
The Fundamental Role of GIS Technology in Mapping
How does GIS serve as the backbone of modern mapping endeavors? GIS, or Geographic Information System, is a technology that combines spatial data with advanced tools for mapping and analysis. Through the integration of various data types, GIS mapping enables a comprehensive understanding of geographic spaces. By leveraging GIS software, professionals can create accurate and dynamic topographic maps, incorporating elevation data, land cover information, and more.
GIS mapping goes beyond static representations, offering a dynamic platform to visualize spatial data. Through the power of GIS, mapping becomes a tool not just for observation but for interpretation, providing valuable insights into the terrain. It’s not merely about drawing lines on a map; it’s about unraveling the intricate relationships within the geographic landscape.

Visualizing Topography in Three Dimensions
How does GIS contribute to the third dimension of mapping? Traditional maps often fall short in capturing the true essence of landscapes. Enter 3D GIS, a cutting-edge technology that elevates mapping to new heights—literally. By integrating elevation data and employing advanced GIS tools, topographic maps can now be visualized in three dimensions. This not only enhances the aesthetic appeal of maps but also provides a more accurate representation of the terrain.
Imagine soaring above mountains, valleys, and rivers with the precision of GIS-generated 3D models. This capability not only aids in aesthetic representation but also proves invaluable in urban planning, environmental monitoring, and disaster management. GIS empowers us to view the world not as a flat surface but as a dynamic, multidimensional space.
Aerial Perspectives and GIS Mapping
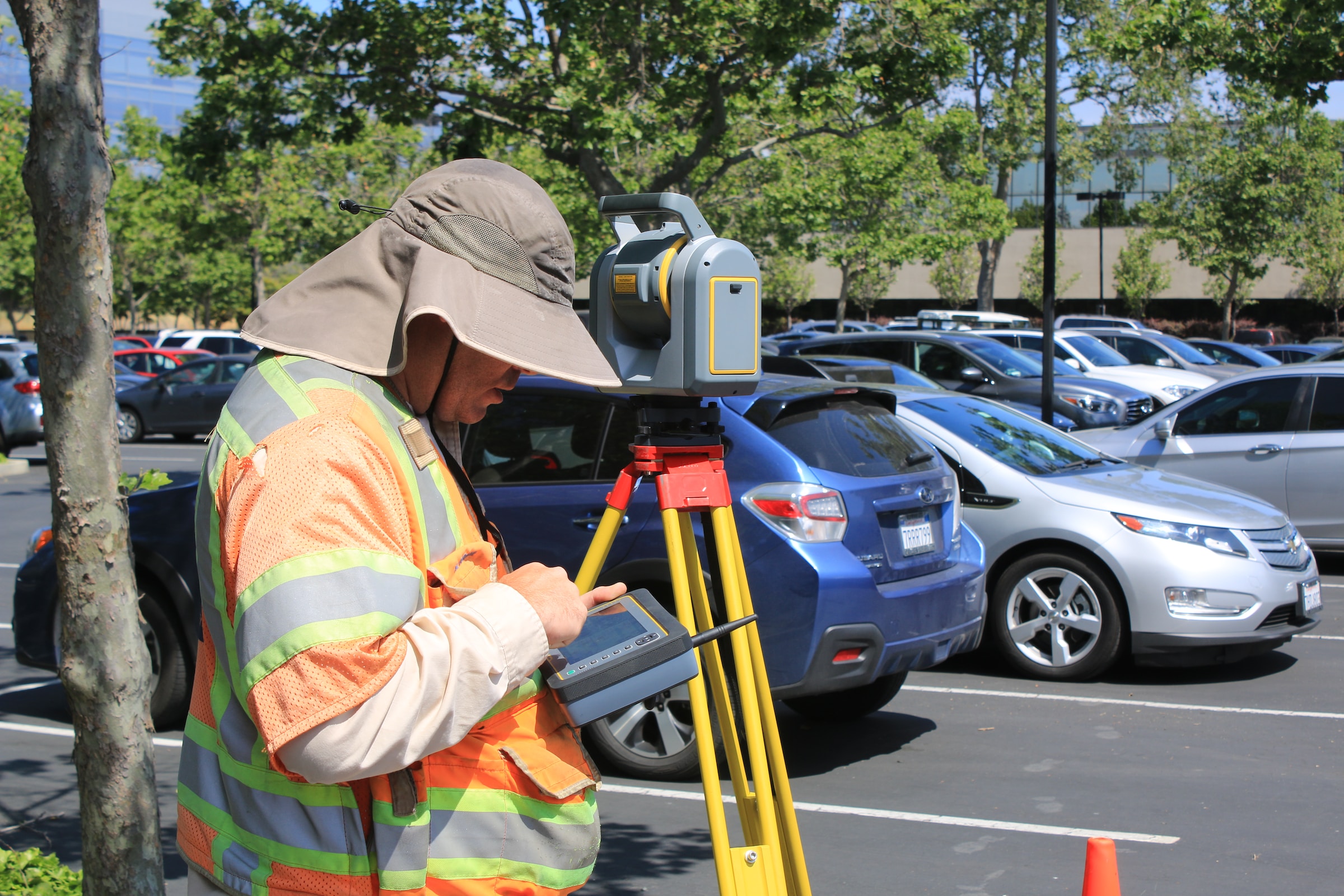
How does GIS harness the power of aerial perspectives for mapping? Aerial imagery, captured through satellites or drones, plays a pivotal role in modern GIS mapping. GIS professionals can integrate high-resolution satellite imagery into their mapping projects, providing a bird’s-eye view of the terrain. This not only enhances the visual appeal of maps but also adds a layer of detail crucial for accurate representation.
GIS mapping tools, such as those offered by Esri, allow users to seamlessly integrate aerial imagery into their projects. Whether it’s assessing land use patterns, monitoring changes over time, or planning infrastructure development, the combination of GIS and aerial perspectives opens new vistas in mapping capabilities.
The Dynamic Web GIS Experience
How does Web GIS transform the accessibility of topographic information? Enter the era of Web GIS, where mapping transcends traditional boundaries. Web GIS allows users to access and interact with maps through web browsers, fostering collaboration and data sharing on an unprecedented scale. With the click of a mouse, users can explore topographic maps, overlay different data sets, and gain valuable insights—all in real-time.
The dynamic nature of Web GIS not only simplifies access but also democratizes the mapping process. No longer confined to specialized GIS professionals, the power of GIS mapping becomes accessible to a broader audience. This democratization is a testament to the transformative impact GIS has on making geographic information available to everyone.
Unveiling the Power of Spatial Analysis
How does GIS contribute to informed decision-making through spatial analysis? Beyond visual appeal, GIS excels in spatial analysis, a process that involves examining the patterns and relationships within geographic data. From determining optimal locations for infrastructure to analyzing the impact of environmental changes, spatial analysis becomes a guiding force in decision-making.
GIS enables professionals to overlay different layers of data, uncovering hidden patterns and correlations. This analytical prowess goes beyond traditional mapping, providing a scientific approach to understanding complex spatial relationships. Harnessing GIS for spatial analysis empowers decision-makers with the knowledge to make informed choices that resonate with the dynamic nature of the landscape.
Leveraging GIS for Data Collection
How does GIS facilitate efficient and accurate data collection? GIS plays a pivotal role in data collection, ensuring that the information incorporated into topographic maps is not only accurate but also up-to-date. Through various data sources, including satellite imagery, sensor data, and field surveys, GIS professionals can gather a diverse range of information to enrich their mapping projects.
The ability to collect real-time data adds a layer of dynamism to topographic maps. Whether it’s monitoring changes in land cover or assessing the impact of natural disasters, GIS data collection tools empower professionals to stay abreast of evolving landscapes. The synergy between GIS and data collection lays the foundation for creating topographic maps that reflect the ever-changing nature of our environment.
Unraveling the Tapestry of Data Sources
How does GIS harness different data sources for comprehensive mapping? GIS is not confined to a singular data type; it thrives on diversity. Topographic maps benefit from the integration of various data sources, including geographic data, satellite imagery, and sensor data. The fusion of these sources allows for a nuanced and detailed representation of the terrain.
GIS professionals can seamlessly integrate vector data, raster images, and real-time data feeds, creating a comprehensive tapestry of information. This multidimensional approach ensures that topographic maps are not only visually appealing but also rich in content. The diversity of data sources enhances the accuracy and reliability of GIS mapping, making it an essential tool for those seeking a holistic view of the landscape.
Navigating the Terrain of Advanced GIS
How does advanced GIS technology redefine the mapping landscape? The evolution of GIS has given rise to advanced technologies that push the boundaries of conventional mapping. From 3D GIS to sophisticated data analysis tools, the realm of advanced GIS opens new possibilities for topographic mapping.
Advanced GIS tools enable professionals to go beyond static representations, allowing for dynamic and interactive mapping experiences. The integration of powerful visualization tools, coupled with the ability to analyze complex spatial relationships, propels GIS into a league of its own. Navigating the terrain of advanced GIS is not just about creating maps; it’s about crafting immersive experiences that convey the intricate details of our geographic landscape.
The Role of GIS in Urban Planning
How does GIS contribute to the planning and development of urban spaces? Urban planning requires a nuanced understanding of the landscape, considering factors such as land use, infrastructure, and environmental impact. GIS emerges as an indispensable tool in urban planning, offering a holistic view of the cityscape.
Through GIS mapping, urban planners can analyze demographic data, assess transportation networks, and model the impact of future developments. This proactive approach facilitates informed decision-making, ensuring that urban spaces are not only aesthetically pleasing but also functionally efficient. The role of GIS in urban planning extends beyond mapping; it becomes a key driver in shaping sustainable and resilient cities.
Crafting Topographic Maps with Specialized GIS
How does specialized GIS contribute to the precision of topographic maps? In the world of GIS, one size does not fit all. Specialized GIS tools cater to specific industries and applications, ensuring that topographic maps meet the precision requirements of diverse sectors. Whether it’s environmental conservation, geological exploration, or infrastructure planning, specialized GIS adds a layer of specificity to mapping endeavors.
Specialized GIS platforms, like those tailored for environmental monitoring or geological mapping, come equipped with tools and functionalities that align with the unique needs of the industry. This specialized approach ensures that topographic maps not only capture the general lay of the land but also provide nuanced insights relevant to specific sectors. The marriage of specialized GIS with topographic mapping refines the accuracy and applicability of GIS in diverse fields.
Conclusion: Mapping the Future with GIS
In conclusion, harnessing GIS for effective topographic map creation transcends the conventional boundaries of mapping. GIS emerges not just as a tool but as a guiding force that shapes our understanding of geographic spaces. From the dynamic perspectives offered by 3D GIS to the democratization of mapping through Web GIS, the journey through the world of GIS mapping is a testament to its transformative power.
As we navigate the terrain of spatial analysis, aerial perspectives, and advanced GIS technologies, it becomes evident that GIS is more than a tool. Whether crafting topographic maps for urban planning or utilizing specialized GIS for industry-specific needs, the applications of GIS are diverse and far-reaching.
In the ever-evolving landscape of geography and mapping, GIS stands as a beacon, guiding us toward a future where topographic maps not only represent the physical contours of our world but also encapsulate the richness and complexity within. As we continue to harness the power of GIS, the journey of topographic map creation becomes a dynamic exploration, shaping the future of cartography in ways we are only beginning to fathom.
Key Takeaways: What to Remember
- GIS is a powerful tool for creating topographic maps, offering dynamic and interactive mapping experiences.
- 3D GIS elevates topographic mapping by providing a multidimensional view of landscapes.
- Aerial perspectives, integrated through GIS mapping, add precision and detail to topographic representations.
- Web GIS democratizes the mapping process, making it accessible to a broader audience.
- Spatial analysis with GIS enables informed decision-making by uncovering patterns and correlations within geographic data.
- GIS facilitates efficient data collection, ensuring accuracy and real-time updates for topographic maps.
- Diverse data sources, integrated through GIS, create a comprehensive tapestry of information for mapping.
- Advanced GIS technologies redefine the mapping landscape, offering immersive and interactive experiences.
- GIS plays a crucial role in urban planning, providing insights for sustainable and resilient cities.
- Specialized GIS tools cater to industry-specific needs, refining the precision and applicability of topographic maps.